Neurodevelopmental centrosomopathies and golgipathies
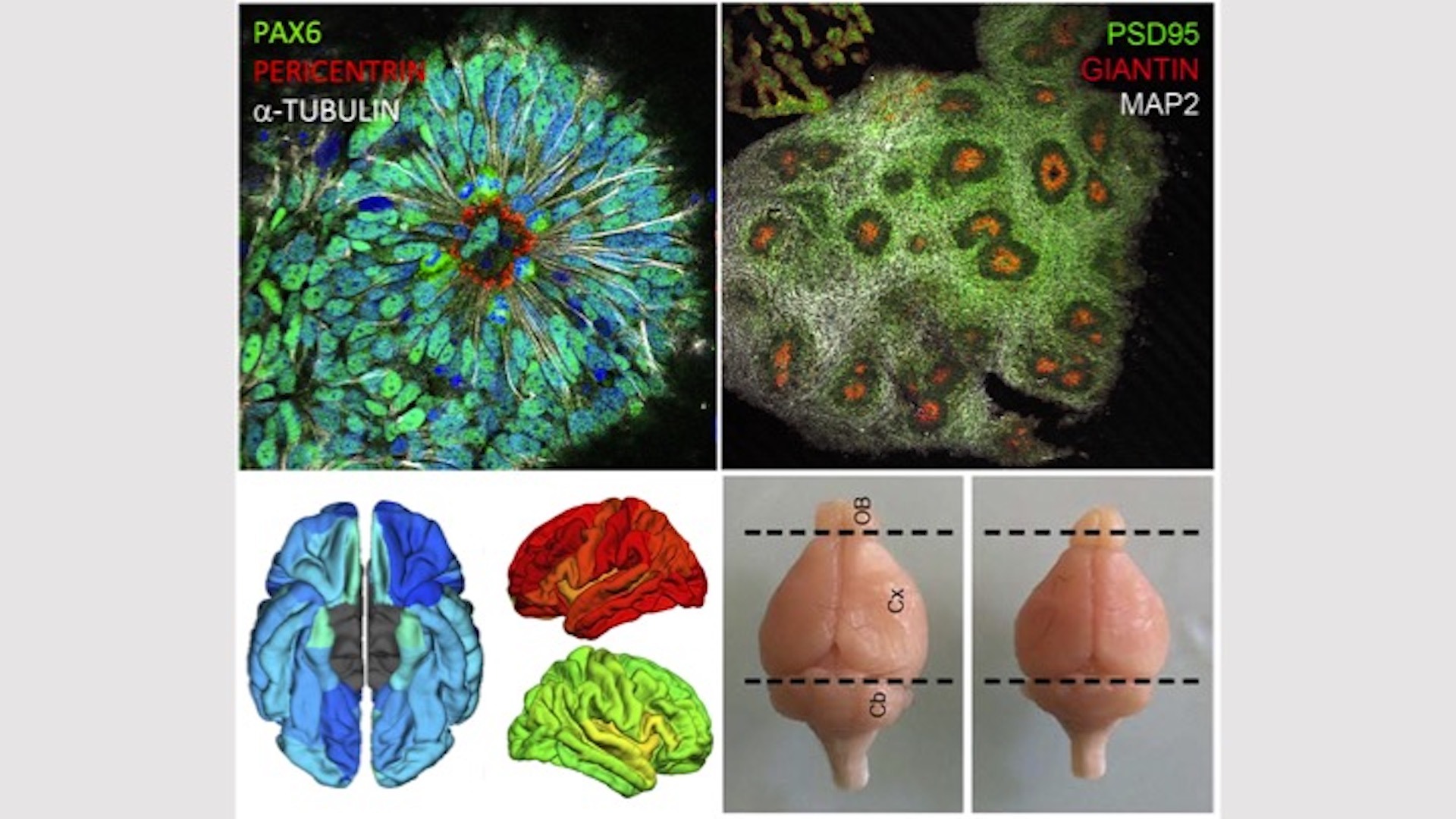
Our group has largely contributed to the identification of several microcephaly genes associated with centrosomopathies (Passemard, Neurology 2009; Nicholas, Nat Genet 2010; Harding, Am J Hum Genet 2016; Létard, Hum Mutat 2018) or Golgipathies (Dimitrov , Hum Mol Genet 2009; Dupuis, Hum Mutat 2013; Izumi, Am J Hum Genet 2016; Uwineza, Eur J Med Genet 2019). The products of genes implicated in centrosomopathies clearly have a role in cell cycle regulation and in the dynamics of the mitotic spindle during the division of neural progenitors, while those of Golgipathies genes appear to be important for the trafficking of pre or post-Golgi vesicles. This suggests that very different patho-mechanisms can lead to microcephaly.
Our group is interested in
i. the phenotypic and molecular characterization of new centrosomopathies and Golgipathies
ii. understanding the pathophysiological roles of the centrosome and the Golgi apparatus in the development of microcephaly
Our experimental approaches include brain imaging, modeling of brain development using organoids derived from human induced pluripotent cells (hiPSCs) from patients and mouse models knocked out for genes of interest.
Members
Albert Alexandra, Inserm Assistant Engineer
Cosson Quentin, PhD Fellow
El Ghouzzi Vincent, CNRS Researcher
Lebon Sophie, Inserm Research Engineer
Masson Justine, CNRS Researcher
Moussay Manon, Inserm Project Engineer
Passemard Sandrine, Professor & Child Neurologist
Ruaud Lyse, PhD Fellow
Verloes Alain, Professor & Geneticist
Main Publications
1. El Ghouzzi V., Boncompain G. Golgipathies reveal the critical role of the sorting machinery in brain and skeletal development Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 7397.
2. Farcy S., Albert A., Gressens P., Baffet A.*, El Ghouzzi V*. Cortical Organoids to Model Microcephaly. Cells, 2022 , 11, 2135. * co-Last
3. Ruaud L., Drunat S., Elmaleh-Berges M., Ernault A., Crepon SG., El Ghouzzi V., Auvin S., Verloes A., Passemard S. Neurological outcome in WDR62 primary microcephaly. Dev. Med Child Neurol., 2022, 64, 509-517.
4. Masson J., El Ghouzzi V. Golgi dysfunctions in ciliopathies Cells, 2022, 11, 2773.
5. Nasser H., Vera L., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Steindl K., Létard P., Teissier N., Ernault A., Guimiot F., Afenjar A., Moutard M.L., Héron D., Alembik Y., Montchilova M., Milani P., Rigaudière F., Kubis N., Pouvreau N., Gressens P., Verloes A., Rauch A., El Ghouzzi V., Drunat S., Passemard S. CDK5RAP2 primary microcephaly is associated with hypothalamic, retinal and cochlear developmental defects. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 389-399
6. Passemard S., Perez F., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stress in microcephaly. Cell Stress, 2019, 3, 369-384.
7. Uwineza A., Caberg J.H., Hitayezu J., Wenric S., Mutesa L., Vial Y., Drunat S., Passemard S., Verloes A., El Ghouzzi V., Bours V. VPS51 biallelic variants cause microcephaly with brain malformations. Eur. J. Med. Genet., 2019, 62, 103704-708.
8. Rasika S., Passemard S., Verloes A., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Golgipathies in neurodevelopment : A new view of old defects. Dev. Neurosci., 2018, 40, 396-416.
9. Létard P., Drunat S., Vial Y., Duerinckx S., Ernault A., Amram D., Arpin S., Bertoli M., Busa T., Ceulemans B., Desir J., Doco-Fenzy M., Chafai Elalaoui S., Devriendt K., Faivre L., Francannet C., Geneviève D., Gérard M., Gitiaux C., Julia S., Lebon S., Lubala T., Mathieu-Dramard M., Maurey H., Metreau J., Nasserereddine S., Nizon M., Pierquin G., Pouvreau N., Rivier-Ringenbach C., Rossi M., Schaefer E., Sefiani A., Sigaudy S., Sznajer Y., Tunca Y., Guilmin Crepon S., Alberti C., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Benzacken B., Wollnick B., Woods G, Rauch A., Abramowicz A., El Ghouzzi V., Gressens P., Verloes A., Passemard S. Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly due to ASPM mutations: an update. Hum. Mutat., 2018, 39, 319-332.
10. Patwardhan D., Mani S., Passemard S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. STIL balancing microcephaly and cancer. Cell Death Dis., 2018, 9, 65-76.
11. Passemard S., Perez F., Colin-Lemesre E., Rasika S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Golgi trafficking defects in postnatal microcephaly: The evidence for “Golgipathies”. Prog. Neurobiol., 2017, 153, 46-63.
12. Cavallin M., Rujano M.A., Bednarek N., Medina-Cano D., Bernabe Gelot A., Drunat S., Maillard C., Garfa-Traore M., Bole C., Nitschké P., Beneteau C., Besnard T., Cogné B., Eveillard M., Kuster A., Poirier K., Verloes A., Martinovic J., Bidat L., Rio M., Lyonnet S., Reilly M.L., Boddaert N., Jenneson-Liver M., Motte J., Doco-Fenzy M., Chelly J., Attie-Bitach T., Simons M., Cantagrel V., Passemard S., Baffet A., Thomas S., Bahi-Buisson N. WDR81 mutations cause extreme microcephaly and impair mitotic progression in human fibroblasts and Drosophila neural stem cells. Brain, 2017, 140, 2597-2609.
13. Passemard S., Verloes A., Billette de Villemeur T., Boespflug O., Hernandez K., Laurent M., Isidor B., Alberti C., Pouvreau N., Drunat S., Gérard B., El Ghouzzi V., Gallego J., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Huttner W.B., Eliez S., Gressens P., Schaer M. Abnormal spindle-like microcephaly (ASPM) mutations strongly disrupt neocortex but spare hippocampus and long-term memory. Cortex, 2016, 74, 158-176.
14. Izumi K., Brett M., Nishi E., Drunat S., Tan E., Fujiki K., Lebon S., Cham B., Masuda K., Arakawa M., Jacquinet A., Yamazumi Y., Chen S., Verloes A., Okada Y., Nakamura T., Akiyama T., Gressens P., Foo R., Passemard S., Tan E., El Ghouzzi V.*, Shirahige K*. ARCN1 mutations cause a recognizable craniofacial syndrome due to COPI-mediated transport defects. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2016, 99, 451-459. * co-Last.
15. Harding B.N., Moccia A., Soukarieh O., Tubeuf H., Drunat S., Chitty L.S., Verloes A., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V., Joriot S., Passemard S., Di Cunto F., Martins A., Bielas S.L. Mutations in Citron Kinase cause recessive microlissencephaly with multinucleated neurons. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2016, 99, 511-520.
16. El Ghouzzi V., Bianchi F.T., Molineris I., Mounce B.C., Berto G.E., Rak M., Lebon S., Aubry L., Tocco C., Gai M., Chiotto A.M.A., Sgrò, Pallavicini G., Simon-Loriere E., Passemard S., Vignuzzi M., Gressens P., Di Cunto F. ZIKA Virus elicits P53 activation and genotoxic stress in human neural progenitors similar to mutations involved in severe forms of genetic microcephaly. Cell Death Dis., 2016, 7, e2440.
17. Dupuis N., Fafouri A., Bayot A., Kumar K., Lecharpentier T., Ball G., Edwards A.D., Bernard V., Dournaud P., Drunat S., Vermelle-Andrzejewski M., Vilain C., Abramowicz M., Désir J., Bonaventure J., Gareil N., Boncompain G., Csaba Z., Perez F., Passemard S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Dymeclin deficiency causes postnatal microcephaly, hypomyelination and reticulum-to-Golgi trafficking defects in mice and humans. Hum. Mol. Genet., 2015, 24, 2771-2783.
18. Srivastava R., Kumar M., Peineau S., Csaba Z., Mani S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Conditional induction of Math1 specifies embryonic stem cells to cerebellar granule neuron lineage and promotes differentiation into mature granule neurons. Stem Cells, 2013, 31, 652-665.
Contacts
Vincent El Ghouzzi, PhD, CRHC CNRS
UMR Inserm 1141 – NeuroDiderot
Hôpital Robert Debré
48 boulevard Sérurier
75019 Paris
vincent.elghouzzi@inserm.fr
Sandrine Passemard, MD PhD, PR Paris 7
Service de Génétique and UMR Inserm 1141 – NeuroDiderot
Hôpital Robert Debré
48 boulevard Sérurier
75019 Paris
sandrine.passsemard@inserm.fr
Read more
Job opportunity within The Integrative Genomics in Neurodevelopment group
The Integrative Genomics in Neurodevelopment group is seeking a highly motivated post-doctoral researcher. Check out the opportunity here: Post-doc researcher position in Computational Biology

Sleep2Develop research program
The Sleep2Develop program investigates the role of sleep as a promotor of neurodevelopment and identifies the sleep determinants of childhood development. This is rephrased as Sleep(to)Develop? or Sleep(to)Develop! Our sleep research combines clinical and...

Job opportunity
NemoClinics platform is hiring an engineer. Check out the opportunity here: U 1141 -Ingénieur-e en expérimentation et instrumentation biologiques- CDD 2023 Read more
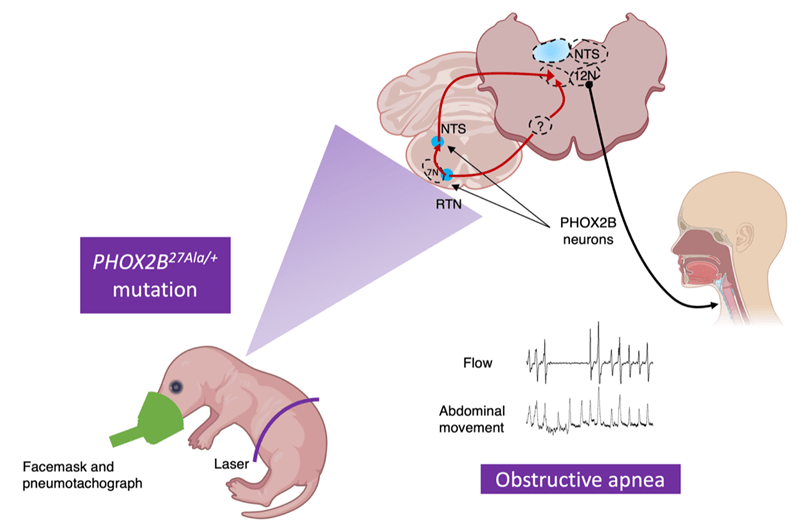
Research program on CCHS
CCHS is a disease characterized by a congenital impairment of the central control of breathing, associated with dysfunctions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) (Gallego, 2012). At birth, patients have severe and persistent hypoventilation during sleep and a...
