Cortical Development & Microcephaly
How the human brain develops from the embryonic stages to adulthood, and how it reaches its final size and organisation, are at the heart of our scientific questions. Our group is interested in cortical development and, in particular, developmental abnormalities that lead to human microcephaly, a relatively common neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests as congenital (primary microcephaly) or postnatal (secondary microcephaly) brain development deficits and can result from genetic variants or environmental causes during pregnancy. To model these pathologies and dissect the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved, we are developing cortical organoids from induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) derived from the cells of patients with microcephaly.
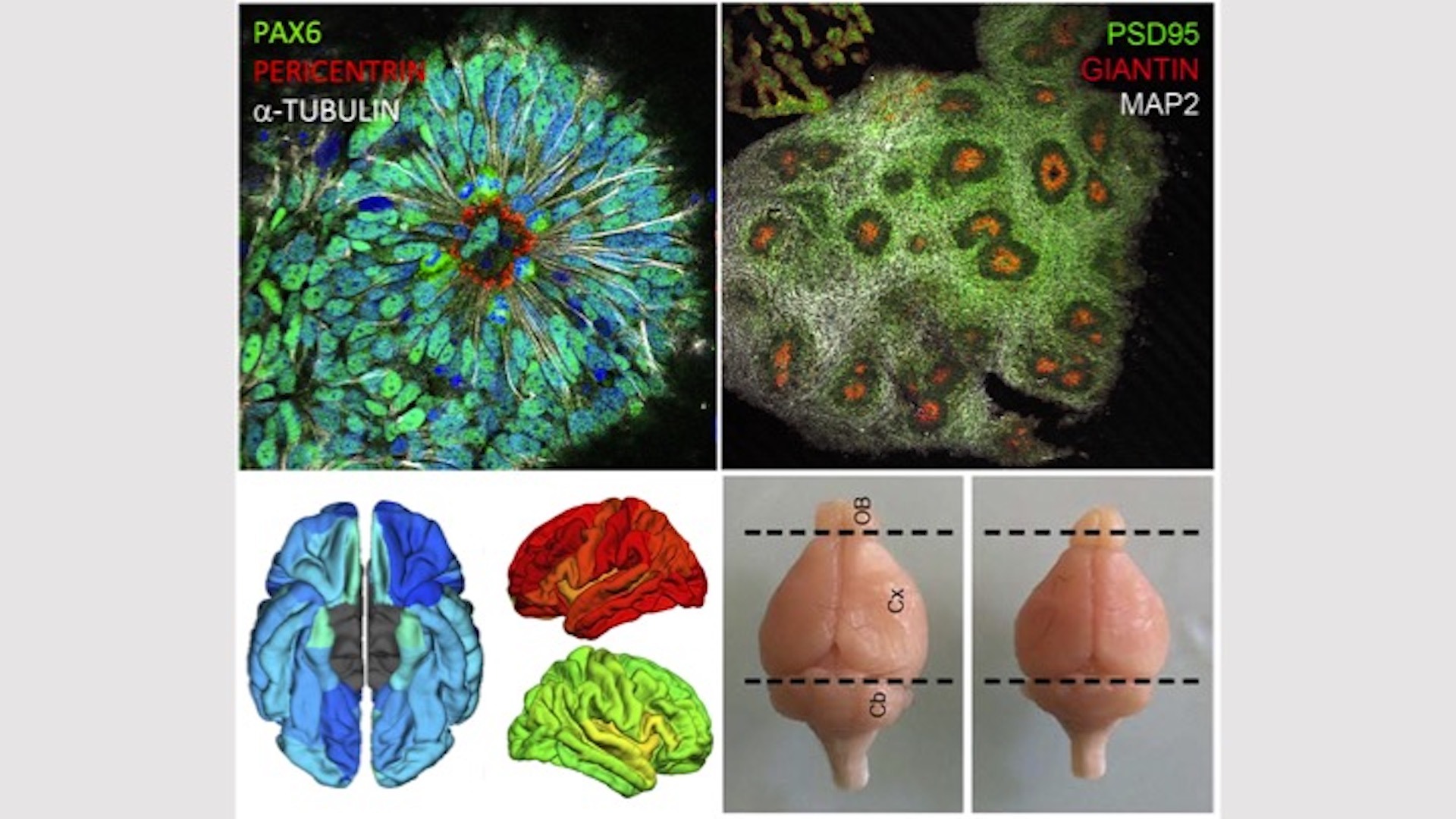
We have identified centrosome defects during corticogenesis and Golgi transport abnormalities as recurrent causes of microcephaly, and our group has contributed significantly to the identification of several microcephaly genes associated with centrosome abnormalities (Passemard, Neurology 2009; Nicholas, Nat Genet 2010; Harding, Am J Hum Genet 2016; Létard, Hum Mutat 2018) or the Golgi apparatus (Dimitrov, Hum Mol Genet 2009; Dupuis, Hum Mutat 2013; Izumi, Am J Hum Genet 2016; Uwineza, Eur J Med Genet 2019). The products of genes involved in centrosomopathies clearly play a role in cell cycle regulation and mitotic spindle dynamics during neural progenitor cell division, while those of Golgipathy genes appear to be important for pre- or post-Golgi vesicle trafficking. This suggests that very different pathomechanisms can lead to microcephaly. Recently, abnormalities in mitochondrial metabolism have also been characterised in certain microcephalies.
Scientific Objectives
Our group is interested in:
1. the phenotypic and molecular characterisation of new centrosomopathies and Golgipathies
2. understanding the pathophysiological roles of the centrosome, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria in the development of microcephaly
Skills & methodology
Our experimental approaches include:
- brain imaging
- Modeling brain development using organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) from patients and genome engineering (CRISPR/Cas)
- Modeling rare disorders in mice with genes of interest knocked out.
- Oxymetry, spectrophotometry ans spectrofluorimetry
Permanent Members
Albert Alexandra, Assistant-Engineer (Inserm)
Drunat Séverine, PH (Hospital)
El Ghouzzi Vincent, Research Director (CNRS)
Jacquier Sandrine, Assistant-Engineer (Inserm)
Lebon Sophie, Research Engineer (Inserm)
Le Guilloux Gwendoline, Assistant-Engineer (Inserm)
Lévy Jonathan, PH (Hospital)
Masson Justine, Researcher (CRHC CNRS)
Moussay Manon, Research Engineer (Inserm)
Papp Bela, Researcher (CRCN Inserm)
Passemard Sandrine, PUPH, Child Neurologist (Hospital)
Rak Malgorzata, Researcher (CRCN CNRS)
Verloes Alain, PUPH (Hospital)
Vial Yoann, MCUPH (Hospital)
Publications
- Albert A., Couture L., Piumi F., Lebon S., Gressens P., Coulpier M., Amara A., El Ghouzzi V*., Meertens L*. Oropouche virus infects human neural progenitor cells and alters the growth of brain organoids. BioRxiv 2025
- Lebon S., Bruneel A., Drunat S., Albert A., Csaba Z., Elmaleh M., Ntorkou A., Ténier Y., Fenaille F., Gressens P., Passemard S., Boespflug-Tanguy O., Dorboz I., El Ghouzzi V. A biallelic variant in GORASP1 causes a novel Golgipathy with glycosylation and mitotic defects. Life Sci. Alliance, 2025 Feb 11;8(4)
- Gins C., Guimiot F., Drunat S., Prévost C., Rosenblatt J., Capri Y., Letard P., Khung-Savatovsky S., Mahi Henni M.A., Chafai Elalaoui S., Alison M., Guilmin Crepon S., Gressens P., Verloes A., Basto R., El Ghouzzi V., Passemard S. Radial microbrain (micrencephaly) is caused by a recurrent variant in the RTTN gene. Neurol. Genet., 2025, 11, e200221.
- Nava C., Cogne B., Santini A., Leitão E., Lecoquierre F., Chen Y., Stenton S.L., Besnard T., Heide S., Baer S., Jakhar A., …, Delahaye-Duriez A…..Passemard S….Depienne C. Dominant variants in major spliceosome U4 and U5 small nuclear RNA genes cause neurodevelopmental disorders through splicing disruption Nat. Genet., 2025 Jun;57(6):1374-1388.
- Pedraza M., Grampa V., Scotto-Lomassese S., Puech J., Muzerelle A., Mohammad A., Lebon S., Renier N., Métin C., Masson J. The ciliary kinesin KIF7 controls the development of the cerebral cortex by acting differentially on SHH-signaling in dorsal and ventral forebrain. eLife, 2025, 13, RP100328.
- Tóth S, Kaszás D, Sónyák J, Tőkés AM, Padányi R, Papp B, Nagy R, Vörös K, Csizmadia T, Tordai A, Enyedi Á. he calcium pump PMCA4b promotes epithelial cell polarization and lumen formation. Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 12;8(1):421.
- Clin. Genet. 2024 Jul;106(1):90-94.
- Adle-Biassette H., Ricci R., Martin A., Martini M., Ravegnini G., Kaci R., Gélébart P., Poirot B., Sándor Z., Lehman-Che J., Tóth E., Papp B. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 3 (SERCA3) expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Pathology. 2024 Apr;56(3):343-356.
- Zatyka M, Rosenstock TR, Sun C, Palhegyi AM, Hughes GW, Lara-Reyna S, Astuti D, di Maio A, Sciauvaud A, Korsgen ME, Stanulovic V, Kocak G, Rak M, Pourtoy-Brasselet S, Winter K, Varga T, Jarrige M, Polvèche H, Correia J, Frickel EM, Hoogenkamp M, Ward DG, Aubry L, Barrett T, Sarkar S. Depletion of WFS1 compromises mitochondrial function in hiPSC-derived neuronal models of Wolfram syndrome. Stem Cell Rep. 2023 May 9;18(5):1090-1106.
- Farcy S., Hachour H., Bahi-Buisson N., Passemard S. Cells, 2023, 12, 1807.
-
Am J Hum Genet. 2023 Apr 6;110(4):663-680.
- El Ghouzzi V., Boncompain G. Golgipathies reveal the critical role of the sorting machinery in brain and skeletal development Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 7397.
- Farcy S., Albert A., Gressens P., Baffet A.*, El Ghouzzi V*. Cortical Organoids to Model Microcephaly. Cells, 2022 , 11, 2135.
- Ruaud L., Drunat S., Elmaleh-Berges M., Ernault A., Crepon SG., El Ghouzzi V., Auvin S., Verloes A., El Ghouzzi V. Neurological outcome in WDR62 primary microcephaly. Dev. Med Child Neurol., 2022, 64, 509-517.
- Masson J., El Ghouzzi V. Golgi dysfunctions in ciliopathies Cells, 2022, 11, 2773.
- Nasser H., Vera L., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Steindl K., Létard P., Teissier N., Ernault A., Guimiot F., Afenjar A., Moutard M.L., Héron D., Alembik Y., Montchilova M., Milani P., Rigaudière F., Kubis N., Pouvreau N., Gressens P., Verloes A., Rauch A., El Ghouzzi V., Drunat S., Passemard S. CDK5RAP2 primary microcephaly is associated with hypothalamic, retinal and cochlear developmental defects. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 389-399
- Diaz J, Gérard X, Emerit MB, Areias J, Geny D, Dégardin J, Simonutti M, Guerquin MJ, Collin T, Viollet C, Billard JM, Métin C, Hubert L, Larti F, Kahrizi K, Jobling R, Agolini E, Shaheen R, Zigler A, Rouiller-Fabre V, Rozet JM, Picaud S, Novelli A, Alameer S, Najmabadi H, Cohn R, Munnich A, Barth M, Lugli L, Alkuraya FS, Blaser S, Gashlan M, Besmond C, Darmon M, Masson J. YIF1B mutations cause a post-natal neurodevelopmental syndrome associated with Golgi and primary cilium alterations. Brain, 2020 Oct 1;143(10):2911-2928.
- Chrétien D, Bénit P, Leroy C, El-Khoury R, Park S, Lee JY, Chang Y-T, Lenaers G, Rustin P, Rak M. Pitfalls in Monitoring Mitochondrial Temperature Using Charged Thermosensitive Fluorophores. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 124
- Passemard S., Perez F., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stress in microcephaly. Cell Stress, 2019, 3, 369-384.
- Uwineza A., Caberg J.H., Hitayezu J., Wenric S., Mutesa L., Vial Y., Drunat S., Passemard S., Verloes A., El Ghouzzi V., Bours V. VPS51 biallelic variants cause microcephaly with brain malformations. Eur. J. Med. Genet., 2019, 62, 103704-708.
- Bénit P, Kahn A, Chretien D, Bortoli S, Huc L, Schiff M, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Favier J, Gressens P, Rak M, Rustin P. Evolutionarily conserved susceptibility of the mitochondrial respiratory chain to SDHI pesticides and its consequence on the impact of SDHIs on human cultured cells. PLoS One 2019 Nov 7;14(11):e0224132
- Benlamara S, Aubry L, Fabregue J, Bénit P, Rustin P, Rak M. Distinctive Krebs cycle remodeling in iPSC-derived neural and mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019 Apr 9;511(3):658-664
- Rasika S., Passemard S., Verloes A., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Golgipathies in neurodevelopment : A new view of old defects. Dev. Neurosci., 2018, 40, 396-416.
- Létard P., Drunat S., Vial Y., Duerinckx S., Ernault A., Amram D., Arpin S., Bertoli M., Busa T., Ceulemans B., Desir J., Doco-Fenzy M., Chafai Elalaoui S., Devriendt K., Faivre L., Francannet C., Geneviève D., Gérard M., Gitiaux C., Julia S., Lebon S., Lubala T., Mathieu-Dramard M., Maurey H., Metreau J., Nasserereddine S., Nizon M., Pierquin G., Pouvreau N., Rivier-Ringenbach C., Rossi M., Schaefer E., Sefiani A., Sigaudy S., Sznajer Y., Tunca Y., Guilmin Crepon S., Alberti C., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Benzacken B., Wollnick B., Woods G, Rauch A., Abramowicz A., El Ghouzzi V., Gressens P., Verloes A., Passemard S. Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly due to ASPM mutations: an update. Hum. Mutat., 2018, 39, 319-332.
- Patwardhan D., Mani S., Passemard S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. STIL balancing microcephaly and cancer. Cell Death Dis., 2018, 9, 65-76.
- Chrétien D, Bénit P, Ha HH, Keipert S, El-Khoury R, Chang YT, Jastroch M, Jacobs HT, Rustin P, Rak M. Mitochondria are physiologically maintained at close to 50 °C. PLoS Biol. 2018 Jan 25;16(1):e2003992
- Passemard S., Perez F., Colin-Lemesre E., Rasika S., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V. Golgi trafficking defects in postnatal microcephaly: The evidence for “Golgipathies”. Prog. Neurobiol., 2017, 153, 46-63.
- Cavallin M., Rujano M.A., Bednarek N., Medina-Cano D., Bernabe Gelot A., Drunat S., Maillard C., Garfa-Traore M., Bole C., Nitschké P., Beneteau C., Besnard T., Cogné B., Eveillard M., Kuster A., Poirier K., Verloes A., Martinovic J., Bidat L., Rio M., Lyonnet S., Reilly M.L., Boddaert N., Jenneson-Liver M., Motte J., Doco-Fenzy M., Chelly J., Attie-Bitach T., Simons M., Cantagrel V., Passemard S., Baffet A., Thomas S., Bahi-Buisson N. WDR81 mutations cause extreme microcephaly and impair mitotic progression in human fibroblasts and Drosophila neural stem cells. Brain, 2017, 140, 2597-2609.
- Bénit P, Chrétien D, Porceddu M, Yanicostas C, Rak M, Rustin P. An Effective, Versatile, and Inexpensive Device for Oxygen Uptake Measurement. J. Clin. Med. 2017 Jun 8;6(6) 58.
- Passemard S., Verloes A., Billette de Villemeur T., Boespflug O., Hernandez K., Laurent M., Isidor B., Alberti C., Pouvreau N., Drunat S., Gérard B., El Ghouzzi V., Gallego J., Elmaleh-Bergès M., Huttner W.B., Eliez S., Gressens P., Schaer M. Abnormal spindle-like microcephaly (ASPM) mutations strongly disrupt neocortex but spare hippocampus and long-term memory. Cortex, 2016, 74, 158-176.
- Izumi K., Brett M., Nishi E., Drunat S., Tan E., Fujiki K., Lebon S., Cham B., Masuda K., Arakawa M., Jacquinet A., Yamazumi Y., Chen S., Verloes A., Okada Y., Nakamura T., Akiyama T., Gressens P., Foo R., Passemard S., Tan E., El Ghouzzi V.*, Shirahige K*. ARCN1 mutations cause a recognizable craniofacial syndrome due to COPI-mediated transport defects. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2016, 99, 451-459.
- Harding B.N., Moccia A., Soukarieh O., Tubeuf H., Drunat S., Chitty L.S., Verloes A., Gressens P., El Ghouzzi V., Joriot S., Passemard S., Di Cunto F., Martins A., Bielas S.L. Mutations in Citron Kinase cause recessive microlissencephaly with multinucleated neurons. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2016, 99, 511-520.
- El Ghouzzi V., Bianchi F.T., Molineris I., Mounce B.C., Berto G.E., Rak M., Lebon S., Aubry L., Tocco C., Gai M., Chiotto A.M.A., Sgrò, Pallavicini G., Simon-Loriere E., Passemard S., Vignuzzi M., Gressens P., Di Cunto F. ZIKA Virus elicits P53 activation and genotoxic stress in human neural progenitors similar to mutations involved in severe forms of genetic microcephaly. Cell Death Dis., 2016, 7, e2440.
Contacts
Vincent El Ghouzzi, PhD, DR2 CNRS
UMR Inserm 1141 – NeuroDiderot
Hôpital Robert Debré
48 boulevard Sérurier
75019 Paris
vincent.elghouzzi@inserm.fr
Sandrine Passemard, MD PhD, PR Paris Cité University
Service de Génétique and UMR Inserm 1141 – NeuroDiderot
Hôpital Robert Debré
48 boulevard Sérurier
75019 Paris
sandrine.passemard@inserm.fr
Read more

Conference April 16th, 2026, 11:00 AM by Alexandra Benchoua from I-Stem : Human pluripotent stem cell models for high-throughput screening of therapeutic molecules and precision medicine in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Meeting Room 6th floor Bingen Building and Visio https://u-paris.zoom.us/j/84730677369?pwd=AFdhdI6alNWLbXub7sM1DJ33yUIOYN.1 - Summary séminaire A-Benchoua _27-nov-2025 english

Scientific conference Melody Atkins Thursday, April 2nd 2026 (11/00 AM).
Meeting Room 6th floor Bingen Building and Visio https://u-paris.zoom.us/j/84730677369?pwd=AFdhdI6alNWLbXub7sM1DJ33yUIOYN.1

Conference Thursday, January 22, 2026, 11:00 AM by Xavier Leinekugel from the Institut de Neurobiologie de la Méditerranée (INMED), Marseille : Potential consequences of altered maturation of hippocampal perisomatic inhibition on cognitive development and neurodevelopmental disorders
20260122 Xavier LEINEKUGEL english

Conference Thursday, February 12 2026, 2PM (zoom) by Pr Raul Chavez-Valdez from Baltimore : Synaptic Plasticity following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
20260212 séminaire Raul Chavez english
